- Home
- Internal Parasites
Understanding Equine Internal Parasites: Types, Impact, and Effective DeWorming Strategies
Horses can be affected by various types of internal parasites, commonly referred to as worms. Each type of worm has its own characteristics and can impact the horse's health in different ways. Here's a list of common types of worms that affect horses and a brief overview of what they can do:
Large Strongyles (Bloodworms):
- Types: Strongylus vulgaris, Strongylus edentatus, Strongylus equinus.
- Impact: Large strongyles can cause damage to the blood vessels in the horse's intestines, leading to colic, weight loss, and general debilitation. Severe infestations may result in arterial blockages and thrombosis.
Small Strongyles (Cyathostomins):
- Types: Various species, including Cyathostomum spp.
- Impact: Small strongyles can encyst in the intestinal lining, causing colic, weight loss, diarrhea, and sometimes damage to the mucosal lining. They are often responsible for larval cyathostominosis, a condition that can be severe and life-threatening.
Roundworms (Ascarids):
- Type: Parascaris equorum.
- Impact: Common in foals, roundworms can cause stunted growth, respiratory issues, colic, and intestinal blockages. In severe cases, heavy infestations may lead to pot-bellied appearance and impede the development of young horses.
Tapeworms:
- Type: Anoplocephala spp.
- Impact: Tapeworms typically attach to the horse's small intestine, leading to irritation and potential blockages. They are associated with colic, weight loss, and digestive disturbances. Regular de-worming targeting tapeworms is crucial to prevent complications.
Bots (Gasterophilus spp.):
- Types: Gasterophilus intestinalis, Gasterophilus nasalis, Gasterophilus haemorrhoidalis.
- Impact: Bots are fly larvae that attach themselves to the stomach lining. While adult bots themselves don't cause significant harm, their larvae can irritate the stomach lining and, in heavy infestations, lead to ulcerations and colic.
Pinworms (Oxyuris equi):
- Type: Oxyuris equi.
- Impact: Pinworms primarily affect the horse's rectum and anus, causing itching and irritation. While they generally don't lead to severe health issues, they can be a source of discomfort and tail rubbing.
It's important for horse owners to work with veterinarians to implement a targeted deworming program based on the specific needs and conditions of their horses. Regular fecal testing can help identify the types and levels of parasites present, allowing for a more strategic and effective deworming approach.
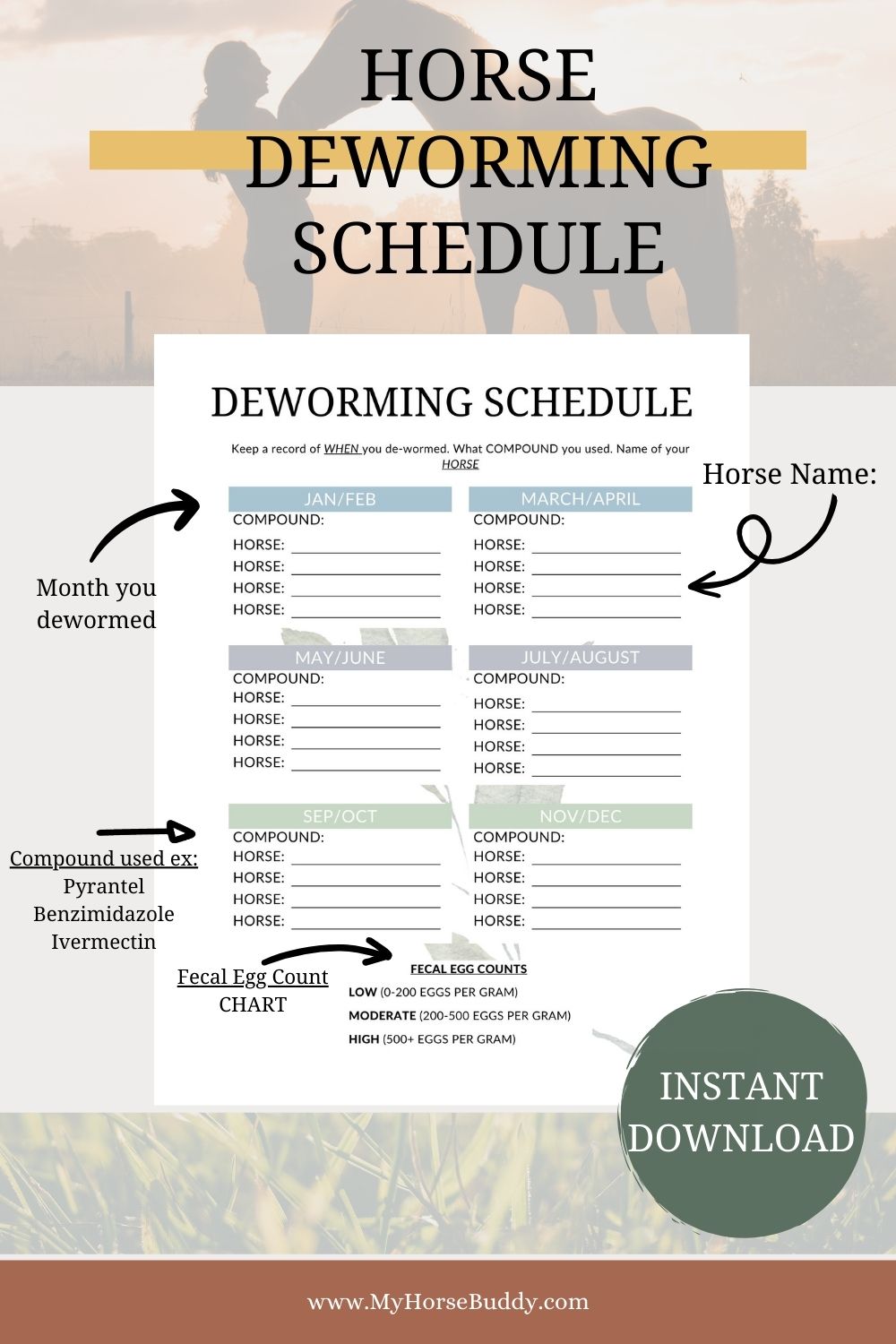
Ready to streamline your horse care routine and ensure your equine companion's well-being? Visit our Etsy shop and download our Deworming Schedule Printable today! Take the first step toward a healthier, happier horse with a well-organized and effective deworming management plan.